No.3916
Net Zero Energy Building (ZEB) Market in Japan: Key Research Findings 2025
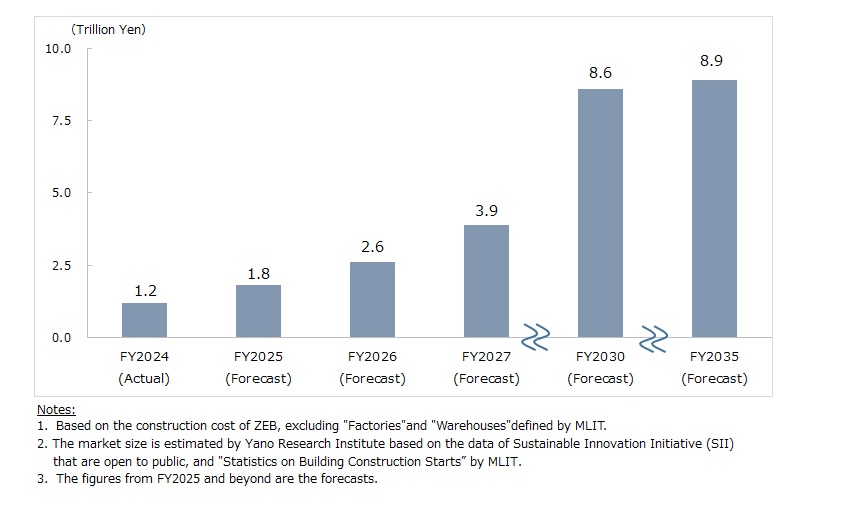
Domestic ZEB Market Forecasted to Reach 8.9 Trillion Yen by FY2035
Yano Research Institute (the President, Takashi Mizukoshi) has conducted a survey on the domestic ZEB market, and found out the market status, company trends, and future perspectives. This press release announces the ZEB market size forecast up to FY2035 (based on the construction cost, excluding “factories” and “warehouses” defined in the Statistics on Building Construction Starts published by MLIT).
Market Overview
In discussions on building decarbonization, it is essential to consider greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions throughout the entire building lifecycle. The building lifecycle can generally be divided into three stages: (1) design and construction, (2) operation and maintenance, and (3) demolition or end-of-life. GHG emissions from stages (1)and (3) are referred to as called Embodied Carbon (EC), while those from stage (2) are referred to as Operational Carbon (OC).
In Japan, builders of non-residential building are encouraged to promote the adoption of expand Net Zero Energy Buildings (ZEBs), i.e., buildings designed to achieve a net zero balance in annual primary energy consumption. In this context, renovating existing buildings to meet ZEB standards contributes to reducing OC during the operation and maintenance stage.
Following the revision of the Environmental Conservation Standard for government facilities, most public buildings constructed after April 2022 meet ZEB Oriented standard or higher*. The shift toward ZEBs is also witnessed in the private non-residential building sector, driven by project owners (such as developers, architects, and building owners) who seek to contribute to environment protection and demonstrate their commitments. Under the circumstances, the size of the domestic ZEB market in FY2024 is estimated at approximately 1.2 trillion yen (based on the construction cost, excluding “factories” and “warehouses” defined in the Statistics on Building Construction Starts published by MLIT).
*ZEB Oriented buildings are non-residential buildings with floor space more than 10,000 square meters that have achieved at least 30 to 40% energy savings (at least 30% in hospitals, department stores, restaurants, and assembly halls, and at least 40% in offices, schools, and factories) and adopted energy-saving technologies that are yet to be evaluated in the current primary energy consumption calculation.
Noteworthy Topics
ZEB Design Support Tool
General construction companies, subcontractors, and architectural companies are strengthening their capabilities to design ZEBs through the development of ZEB design support tools. Typically, designing a ZEB involves using a web-based energy simulation program (WEBPRO) to calculate on-site energy consumption, including HVAC, lighting, hot water supply, etc. However, because detailed specifications are often not finalized in the early design stages, and using WEBPRO requires significant time and effort, streamlining the calculation process has long been a challenge for businesses seeking to increase their number of ZEB projects.
Against this background, some general construction companies, subcontractors, and architectural firms have begun developing design support tools to accelerate environmental performance verification, using legacy ZEB design data and Building Information Modeling (BIM) *. The system incorporates tools that automatically select appropriate building envelope materials and equipment for achieving ZEBs by extracting data on building envelopes and floor areas from architectural drawings. This approach not only allows decision making on specs and costs for ZEB compliance from the early design stages but also accelerates the process of adapting to design changes.
* Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a 3D model -based system for digitally integrating data about building's physical and functional characteristics.
Future Outlook
Alongside Japan’s Seventh Strategic Energy Plan, which sets a goal for all new non-residential buildings to meet ZEB standards by FY2030, ZEB adoption continues to attract significant attention.
The Plan also aims to achieve ZEB-level energy efficiency across the entire building stock by 2050, which will require extensive renovation of existing buildings. Under the circumstances, the ZEB market in Japan is forecasted to reach approximately 8.6 trillion yen by FY2030, and 8.9 trillion yen by FY2035 (based on the construction cost, excluding “factories” and “warehouses” defined in the Statistics on Building Construction Starts published by MLIT).
Currently, building decarbonization primarily focuses on reducing Operational Carbon (OC). However, the ultimate goal is to achieve net zero Whole Life Carbon (WLC), including both Embodied Carbon (EC) and OC across the building’s entire lifecycle. To support this objective, the government plans to launch a “Building Life Cycle Assessment (LCM) System” by FY2028, mandating construction companies to calculate and disclose WLC. Going forward, general construction companies, subcontractors, and architectural firms in the non-residential sector will need to reduce EC during the design and construction stage as well as demolition (end-of-life) stage, by using construction materials with lower climate impact and providing maintenance solution that extend building’s lifecycle.
Research Outline
2.Research Object: General construction companies, subcontractors, and architectural firms that have extensive experience in designing and/or constructing ZEBs
3.Research Methogology: Face-to-face interviews by our expert researchers (including online interviews) and literature research
ZEB Market
According to the ZEB Roadmap Examination Committee under the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy (METI), Net Zero Energy Building (ZEB) is defined as a building designed to achieve a net zero balance in annual primary energy consumption through a combination of advanced architectural design, passive and high-efficiency technologies, and renewable energy systems, all while maintaining the quality of the indoor and outdoor environments.
In this research, the ZEB market includes non-residential buildings designed by ZEB planner (companies pertaining to designing ZEB), which meets one of the ZEB standards (“THE ZEB”, Nearly ZEB, ZEB Ready, or ZEB Oriented), and the market size is calculated based on the construction costs for ZEB. In this context, non-residential buildings refer to categories such as “Offices,” “Stores,” “Schools,” “Hospitals,” and “Others,” as defined in the Statistics on Building Construction Starts by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT). Unlike the previous survey conducted in 2023, “Factories” and “Warehouses” are excluded, as ZEB Ready and ZEB certification thresholds for these facilities are assessed only for improvements made to their office areas, not the entire site. For this reason, their monetary impact on the overall ZEB market size is considered negligible.
<Products and Services in the Market>
Net Zero Energy Building (ZEB)
Published Report
Contact Us
The copyright and all other rights pertaining to this report belong to Yano Research Institute.
Please contact our PR team when quoting the report contents for the purpose other than media coverage.
Depending on the purpose of using our report, we may ask you to present your sentences for confirmation beforehand.