No.3911
Last-Mile Delivery (Logistics) Market in Japan: Key Research Findings 2025
Last-Mile Delivery Market Size Reached 3,090 Billion Yen in FY2024, a 5.5% Increase From Previous Fiscal Year
Yano Research Institute (the President, Takashi Mizukoshi) carried out a survey on the domestic last-mile delivery (logistics) market and found out the trends by category, trends of market players, and future perspectives.
Market Overview
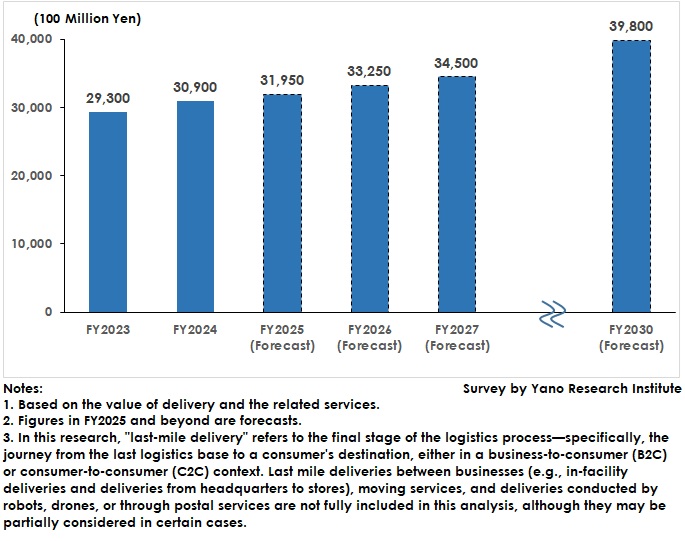
Based on delivery fees and the value of related services, the last-mile delivery market was estimated at 3,090 billion yen in FY2024, representing 105.5% of the previous year’s size. This growth was driven by an overall increase in parcel volume and rate hikes among last-mile delivery operators, excluding home delivery companies, which experienced volume growth but not higher rates.
A surge in parcel volumes was observed particularly among mail-order businesses. The number of parcels increased due to the trend of splitting shipments into smaller packages. Following price negotiations amid serious labor shortages and soaring fuel costs, the cost of last-mile deliveries has risen moderately.
However, major home delivery companies temporarily reduced corporate contract prices and increased parcel volumes in FY2024, after experiencing a decline in deliveries following price revisions in FY2023.
B2C delivery service providers, excluding home delivery companies, include mail-order businesses, retailers operating online supermarkets and convenience stores, and food delivery service providers. The number of these businesses is increasing, driven by a shift among major mail-order businesses toward in-house delivery instead of using home delivery companies, as well as by rising last-mile delivery costs.
Noteworthy Topics
Last-Mile Delivery Market Share by Delivery Type
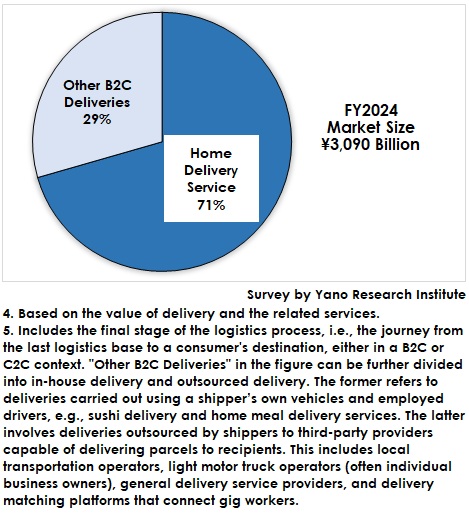
This research defines two types of delivery within the last-mile delivery market: 1) home delivery categorized as "special group cargo motor trucking (commissioned home delivery)", and 2) B2C or last-mile delivery services excluding home delivery. In FY2024, home delivery services accounted for 70% of the market by value, while other B2C services accounted for the remaining 30%.
The latter category—other B2C delivery services—can be further divided into two subtypes: in-house delivery and outsourced delivery.
- In-house delivery refers to deliveries carried out using a shipper’s own vehicles and employed drivers. Typical examples include sushi delivery and home meal delivery services.
- Outsourced delivery involves deliveries outsourced by shippers to third-party providers capable of delivering parcels to recipients. This includes local transportation operators, light motor truck operators (often individual business owners), general delivery service providers, and delivery matching platforms that connect gig workers—contracted on an hourly, daily, or per-project basis—with delivery tasks.
Home delivery companies are often commissioned for the entire process, including warehousing and delivery, and all last-mile delivery processes when parcel volumes are insufficient to justify in-house shipping arrangements. They are also relied on for temperature-sensitive deliveries, such as frozen or refrigerated items, as well as deliveries with date and time specifications, including redelivery requests, and deliveries tailored to products and users' needs.
Other B2C delivery operators, excluding home delivery companies, are often chosen for delivery opportunities involving a certain amount of parcel volume. They are also chosen for deliveries that allow parcels to be left at the door when recipients are not home, and for added-value deliveries, such as immediate delivery right after ordering and safety confirmation services, which is to check residents' health conditions. Mail-order businesses often use these services because they allow parcels to be left at doors. This has resulted in an increase in the outsourcing delivery commissions to local transportation operators and light motor truck operators.
Future Outlook
The last-mile delivery market is forecast to reach 3,195 billion yen in FY2025, representing 103.4% of the previous year’s size. This growth is driven by new sources of demand, such as cross-border e-commerce deliveries–particularly for items purchased on Chinese and Korean shopping sites–and hometown tax return gift deliveries. Continued trends in shipment splitting, which increase the number of parcels, are also contributing to the market’s expansion.
Since the end of the pandemic, home delivery companies have experienced a gradual increase in B2C deliveries compared to B2B deliveries every year. Since spending per customer is expected to increase, the ongoing shift to B2C deliveries is likely to continue at a moderate pace in FY2025 and beyond. Meanwhile, mail-order businesses are expected to accelerate the outsourcing of deliveries to last-mile delivery operators (other than home delivery companies) and increase their parcel volumes. Consequently, the last-mile delivery market is expected to reach 3,980 billion yen by FY2030.
The challenge of last-mile deliveries lies in establishing regulations for “other B2C delivery operators.” These businesses, excluding home delivery companies, are not subject to home delivery rules. Without rules, problems may arise. Some rules must be established as standards from a broad framework, including delivery quality and driver compensation.
Research Outline
2.Research Object: Businesses providing B2C and C2C delivery services.
3.Research Methogology: Face-to-face interviews by expert researchers, survey via telephone, and literature research
The Last Mile Delivery (Logistics) Market
In this research, "last-mile delivery (logistics)" refers to the final stage of the logistics process—specifically, the journey from the last logistics base to a consumer's destination, either in a business-to-consumer (B2C) or consumer-to-consumer (C2C) context. The market size is calculated based on delivery fees and the value of related services.
Please note that last-mile deliveries between businesses (e.g., in-facility deliveries and deliveries from headquarters to stores), moving services, and deliveries conducted by robots, drones, or through postal services are not fully included in this analysis, although they may be partially considered in certain cases.
<Products and Services in the Market>
Last-mile delivery business that involves deliveries between businesses to customers, and between customers, e.g., home delivery services, individual B2C delivery (in-house delivery, local transporters, light motor truck transporters, and other delivery services.) Gig-work delivery dispatched by delivery matching service providers are also included.
Published Report
Contact Us
The copyright and all other rights pertaining to this report belong to Yano Research Institute.
Please contact our PR team when quoting the report contents for the purpose other than media coverage.
Depending on the purpose of using our report, we may ask you to present your sentences for confirmation beforehand.