No.3689
Major (Non-Agricultural) Companies Entering Agricultural Business in Japan: Key Research Findings 2024
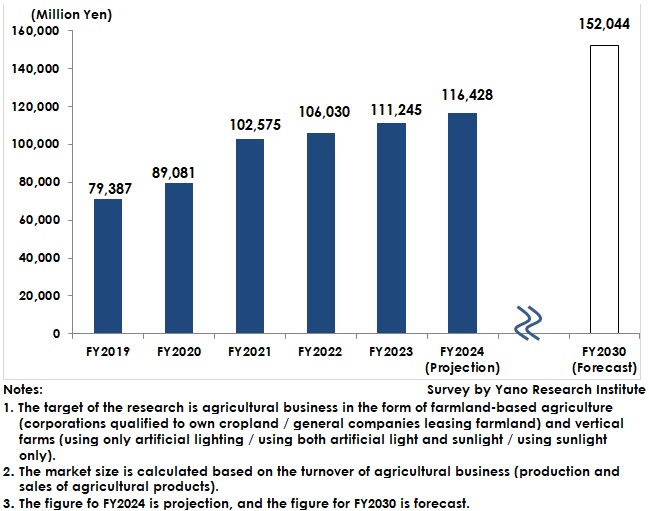
Agricultural Business Market by Major Domestic Non-Agricultural Companies Estimated to Have Expanded to 104.7% of Previous Fiscal Year' Size to 116,428 Million Yen in FY2024
Yano Research Institute (the President, Takashi Mizukoshi) has conducted a survey on the trends of major domestic companies entering agricultural business (from non-agricultural industries), and found out the market size, the trends of market players, and future perspectives.
Market Overview
The agricultural business of leading domestic non-farming companies is estimated to be 111,245 million yen in FY2023, 104.9% of the previous fiscal year.
Supported by the government's promotion of the growth strategy and for becoming the sixth industry, as well as initiatives for stable food supply, entry into the agricultural business has been in the spotlight among major companies in Japan. Production risks stemming from climate change and expanding business demand for agricultural products in the revitalized ready-to-eat food and food service industries are driving entry into the business. While there is a problem of expansion of abandoned farmland due to withdrawal from agriculture, entry into the agricultural business by non-farming companies is expected to contribute to solving labor shortages and effective use of farmland.
Enterprises that enter agriculture from other industries use their own techniques that have been developed in their main business in harvesting or sorting in agricultural tasks, which results in building an efficient agricultural production system. Such a move has attracted attention as a method of revitalizing agriculture and can lead to new business opportunities.
Noteworthy Topics
Outline of Regenerative Agriculture and Its Challenges in Japan
Regenerative agriculture is a farming approach that aims to regenerate the natural environment and presupposes organic agriculture that does not use chemical fertilizers and chemical pesticides. The approach includes no-till practices to store carbon in the soil and cover crops, which are expected to maintain soil health by reducing soil drainage and physically improving the soil.
There are few examples of regenerative agriculture in Japan, and it is far from widespread, despite the introduction of regenerative organic certification. Many of the companies we interviewed said that while they feel the need to be environmentally responsible, they face cost challenges in doing so. In addition, there are many vague cases of not being able to see the clear distinction between regenerative agriculture and other environmentally conscious agriculture in Japan. Furthermore, protected horticulture and hydroponics in vertical farming cannot be included in regenerative agriculture, making it one of the challenges for producers engaged in these approaches to participate in regenerative agriculture.
According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF), the area of organic agriculture in Japan has been expanding, but still remains to be 30.3 thousand hectares, or less than one percent of the total arable land, as of the end of 2022. Further promotion of regenerative agriculture is expected through improved awareness and increased entry by proactive companies.
Future Outlook
The agricultural business of leading domestic non-farming companies is estimated to be 116,428 million yen in FY2024, 104.7% of the previous fiscal year. The willingness of companies to enter the market remains high due to progress in the effective use of farmland and deregulation. The vertical farming business has driven the overall market by responding to users with stable supply as it is hardly affected by weather.
The entry of companies from various industries not only revitalizes agriculture but also improves production efficiency. Even in regions where people have withdrawn from agriculture, companies that have entered the agricultural business are expected to utilize abandoned land and improve regional production levels.
The agricultural business of leading domestic non-agricultural companies is forecast to reach 152,044 million yen by FY2030. Companies that have entered the market are expected to explore overseas markets from now on. In such a situation, market entry by those companies with new visions beyond agriculture can play an increasingly important role.
Research Outline
2.Research Object: Major companies (non-agricultural enterprises) entering agricultural business (production and sales of farm produce), and related domestic institutions
3.Research Methogology: Face-to-face interviews (including online) by our expert researchers, surveys via email/telephone, and literature research
What is the Agricultural Business by Domestic Major Non-Farming Entities?
While there is no clear definition for “agricultural business” or "agribusiness," it generally refers to the production and distribution of agricultural products, as well as to the business that provides services using ICT for agriculture. In this research, “agricultural business” refers to the production and sales of farm produce by major domestic enterprises that have entered the market from industries traditionally unrelated to agriculture. The target of the research is agricultural business in the form of farmland-based agriculture (corporations qualified to own cropland / general companies leasing farmland) and vertical farms (using only artificial lighting / using both artificial light and sunlight / using sunlight only). Farmers who have incorporated their farms are excluded.
The market size is calculated based on the turnover of agricultural business (production and sales of agricultural products).
<Products and Services in the Market>
Farmland-based agriculture (corporations qualified to own cropland / general companies leasing farmland), vertical farms (using only artificial lighting / using both artificial light and sunlight / using sunlight only)
Published Report
Contact Us
The copyright and all other rights pertaining to this report belong to Yano Research Institute.
Please contact our PR team when quoting the report contents for the purpose other than media coverage.
Depending on the purpose of using our report, we may ask you to present your sentences for confirmation beforehand.