No.3759
Global Market for Automotive Silicon Carbide (SiC) Power Modules: Key Research Findings 2024
The Global Market for Automotive (xEV) SiC Power Modules Forecast to Reach 758.6 Billion yen by 2035, Driven by the Prevalence of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
Yano Research Institute (the President, Takashi Mizukoshi) surveyed the global market for automotive (xEV) power modules and found out the market overview, adoption trends, business strategies of individual manufacturers, and forecasted the global market size.
Market Overview
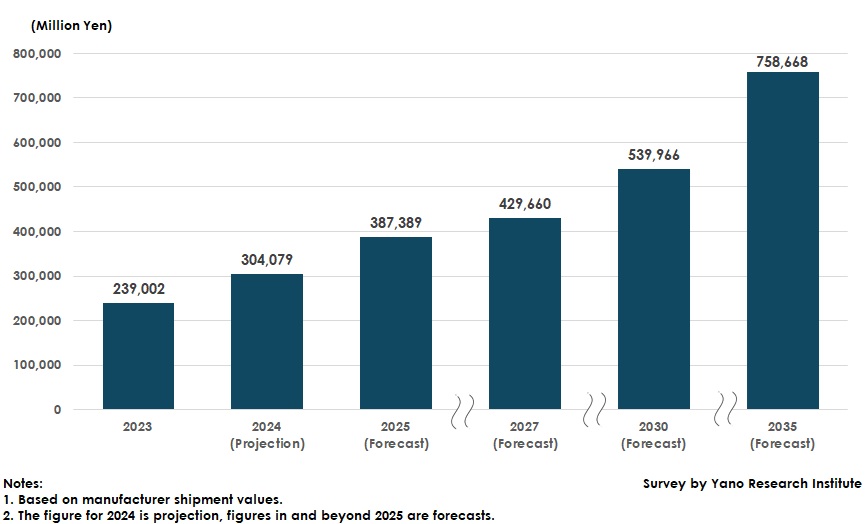
Based on manufacturer shipment values, the global market size of silicon carbide (SiC) power modules (PMs) for eXtended electric vehicles (xEVs), which include hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and battery electric vehicles (BEVs), is expected to reach 304.079 billion yen in 2024, a 27.2% increase from the previous year, due to increased global xEV sales.
Previously, SiC inverters with SiC PMs were only installed in large, luxury BEVs and in vehicles from emerging BEV manufacturers. However, they will likely be installed in a wider range of vehicle types, starting from new BEVs released in the second half of 2025 and through 2027.
Noteworthy Topics
Trends in Silicon Carbide (SiC) Power Module Adoption in Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
The number of silicon carbide (SiC) power modules (PMs) in a vehicle depends on the structure of its drive motor. All-wheel drive vehicles (AWD vehicles) require motors at the front and the rear, whereas front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles require a motor at the front, and rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles require a motor at the rear.
An AWD structure is adopted in large, luxury BEVs, in which inverters are needed one each at the front and rear, so the maximum number of SiC PMs installed is two. If SiC PMs are used in both the front and rear inverters, then two PMs are used. Sometimes, one SiC PM is used in either the front or rear and is coupled with a silicon (Si) PM in the other.
The number of inverters for a FWD vehicle or a RWD vehicle requires one, which is widely seen in small or medium-sized BEVs. In these cases, Si PMs are usually used, as they are less expensive. However, some automakers use SiC PMs to extend electric range by improving inverter performance and reducing power supply losses from the battery to the motor.
Future Outlook
The global market size of silicon carbide (SiC) power modules (PMs) for xEVs is forecast to reach 758.668 billion yen based on manufacturer shipment values, due to the continued proliferation of xEVs.
Since the late 2020s, SiC inverters have become widely used in eAxles, drive units that integrates a drive motor, decelerator, and inverter, primarily for BEV platforms whose development is in progress by automakers. This adoption is surging in demand in the SiC PM market. Full adoption of inverters embedded with SiC PMs will likely occur not only in large, luxury BEVs, but also in medium-sized sport utility vehicle (SUVs) with AWD.
Because of their high efficiency and low power loss, SiC PMs are expected to increase electric range with a single charge. They also generate less heat, enabling a simple cooling structure and allowing inverters to be thinner. This minimizes the size of the eAxle, creating room for a flexible layout and expanding interior space in cars.
Since the late 2020s, expanded production capacity among power semiconductor manufacturers and advancements in mass production technologies have likely reduced the cost of SiC PMs. This reduction will likely lead to the adoption of SiC PMs in plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), in addition to BEVs.
Currently, PHEVs face challenges in improving electric-range efficiency, i.e., the battery-powered driving range of motors. Integrating highly efficient SiC PMs into inverters can enhance electric range and improve fuel efficiency. Since China is expected to increase PHEV sales, automakers are eagerly developing the next-generation PHEVs with electric-range-focused designs.
After 2030, the demand for SiC PMs for PHEVs is expected to surge as they are applied to some PHEV models, which will boost the global market size of SiC PMs for xEVs.
Research Outline
2.Research Object: Automakers, tier-1 auto parts manufacturers, power semiconductor manufacturers
3.Research Methogology: Face-to-face (including online) and phone interviews by expert researchers and literature research
What are Automotive Power Modules?
Automotive power modules (PMs) are components needed to convert electricity for motor vehicles, mainly used as inverters for hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) and battery electric vehicles (BEVs). These vehicles require inverters to convert the direct current (DC) from the battery to alternating current (AC) for the propulsion system. Inverter components include an automotive power module, various passive components, a control board, and a cooling device. An automotive power module (PM) is a modularized power semiconductor chip, specifically an Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT).
Advances in technology innovation have improved conversion efficiency, and automotive power modules that use silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors are gaining attention alongside conventional IGBTs that use silicon (Si) semiconductors.
In HEVs and BEVs, an eAxle drive unit, which integrates a drive motor, decelerator, and inverter, is installed at the front, and sometimes also at the rear, if it is a four-wheel drive vehicle. An SiC power module is embedded in the eAxle.
<Products and Services in the Market>
Power modules for xEVs (Si power module, SiC power module), Si power semiconductor, SiC power semiconductor
Published Report
Contact Us
The copyright and all other rights pertaining to this report belong to Yano Research Institute.
Please contact our PR team when quoting the report contents for the purpose other than media coverage.
Depending on the purpose of using our report, we may ask you to present your sentences for confirmation beforehand.