Japanese Food Makers in China and ASEAN Countries: Key Research Findings 2016
Research Outline
- Research period: December, 2016
- Research target: 61 Japanese food makers which have overseas production bases (including consignment production) mainly in China and ASEAN countries (i.e., Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Philippines, Vietnam, Myanmar, and Cambodia)
- Research methodologies: Interview via telephone (conducted in Japan)
<About Questionnaire to Japanese Food Makers Operating Overseas Production Bases Mainly in China and ASEAN Countries >
This questionnaire has been conducted to the Japanese food makers by means of telephone interviews regarding their procurement and production of ingredients and materials, and final destination at overseas production bases mainly in China and ASEAN countries. This report covers the research and analysis regarding production structures and the quality of the local ingredient and material suppliers.
The ASEAN countries in this research indicate the following eight countries: Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Philippines, Vietnam, Myanmar, and Cambodia.
Summary of Research Findings
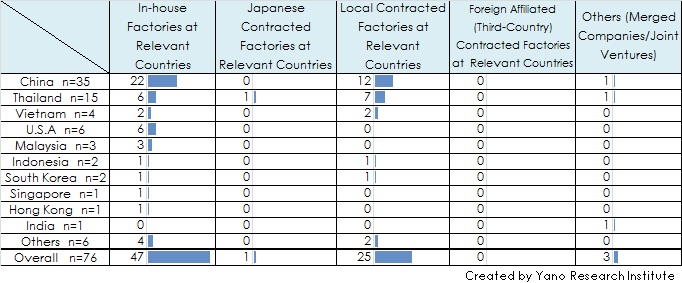
- More than 50% of Japanese Food Makers with Their Production Base in Thailand Use Consignment Production
With regard to the production base of the Japanese food makers in Thailand, the ratio of in-house factories (including affiliated companies) are 40% (6 out of total 15 bases in Thailand,) which is lower than the ratio of contracted factories accounting for 53.3%, the ratio of total 1 Japanese and 7 local contracted factories. It indicates that there are many cases of Japanese food makers that develop business in Thailand use consignment production rather than operating their own in-house factories.
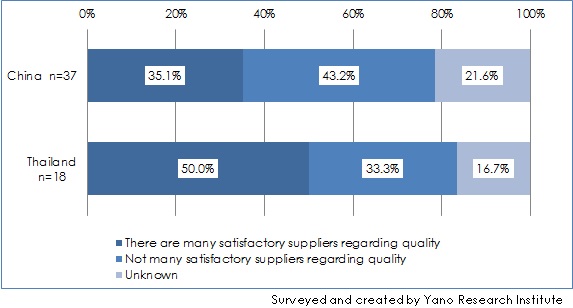
- More than 40% Responded that There are Not Many Satisfactory Ingredient/Material Suppliers in China
To the questions regarding the quality of the ingredient and material suppliers in China, 35.1% of the respondents said that “there are many satisfactory ingredient/material suppliers in China,” whereas 43.2% said that “there are not many.” This indicates that the number of Japanese food makers who feel discontented with the quality of the local suppliers in China exceeded those who don’t.
- Table 1: Production Structure of Japanese Food Makers at Overseas Production Bases by Nation/Region
- Figure 2: Quality Assessment of Local Ingredients/Materials Suppliers in China and Thailand