No.3848
Global Motorbike Market: Key Research Findings 2025
The Electrification Rate of Two-Wheel Vehicles Expected to Grow to Maximum 15% by 2030
Yano Research Institute (the President, Takashi Mizukoshi) conducted a survey on the global motorbike market and provided the market overviews in major countries and the trends of major manufacturers. This paper highlights the global motorbike sales and motorbike electrification rate through 2035.
Market Overview
2024 saw both growth and deceleration.
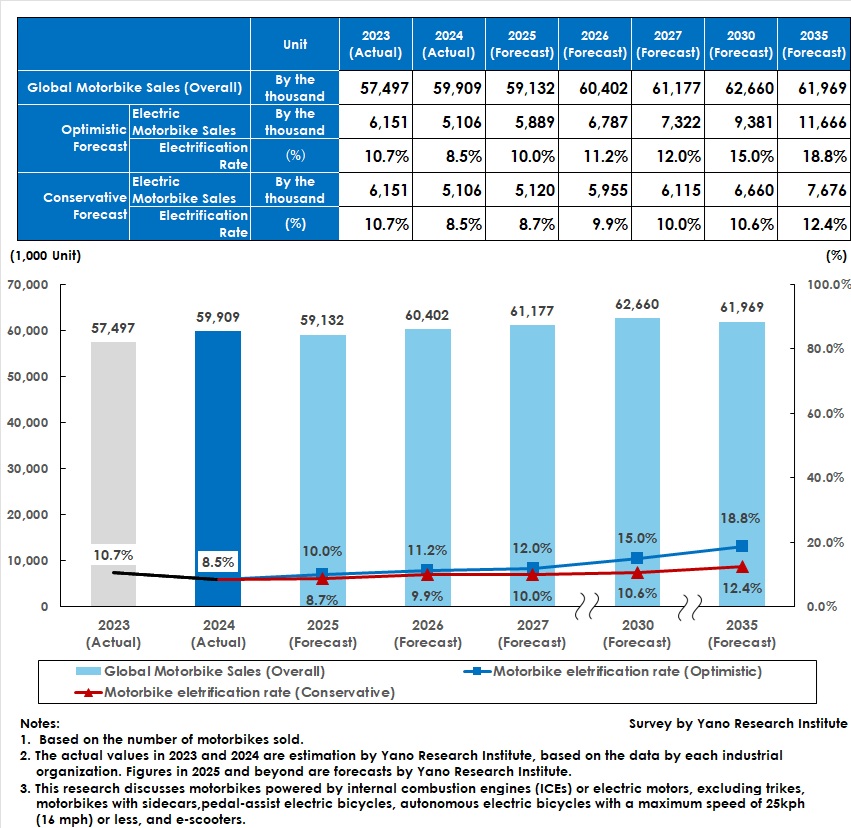
In 2024, global new motorbike sales steadily grew to 59.909 million units, a 4.2% rise from the previous year. India was the growth driver, reaching 19.54 million units, a 11.5% increase from the previous year, establishing itself as the world's largest market. This growth was fueled by increased demand in rural areas and the Prime Minister's Gati Shakti initiative (also known as the National Master Plan for Multi-modal Connectivity), which accelerated government spending. Pakistan and Brazil also enjoyed favorable sales, and ASEAN countries recovered in terms of exports and domestic demand. All countries grew from the previous year except for Thailand, where a sharp rise in household debt led to more stringent loan screening.
Conversely, global new sales of electric motorbikes, including electric mopeds, decreased from 6.151 million units in 2023 to 5.106 million units in 2024. This reduced the electric motorbike penetration rates from 10.7% in 2023 to 8.5% in 2024. The primary reason for the decline was the fallen sales in China, the largest electric motorbike market. The growth in India and Indonesia could not cover the loss.
Amidst global inflation and political uncertainty, the total cost of ownership (TCO) of two-wheelers, as well as their flexibility as a personal mobility solution, have been reevaluated. Following the widespread popularity of two-wheelers as a common method of transportation in emerging countries, the usability of electric motorbikes has been reevaluated.
Noteworthy Topics
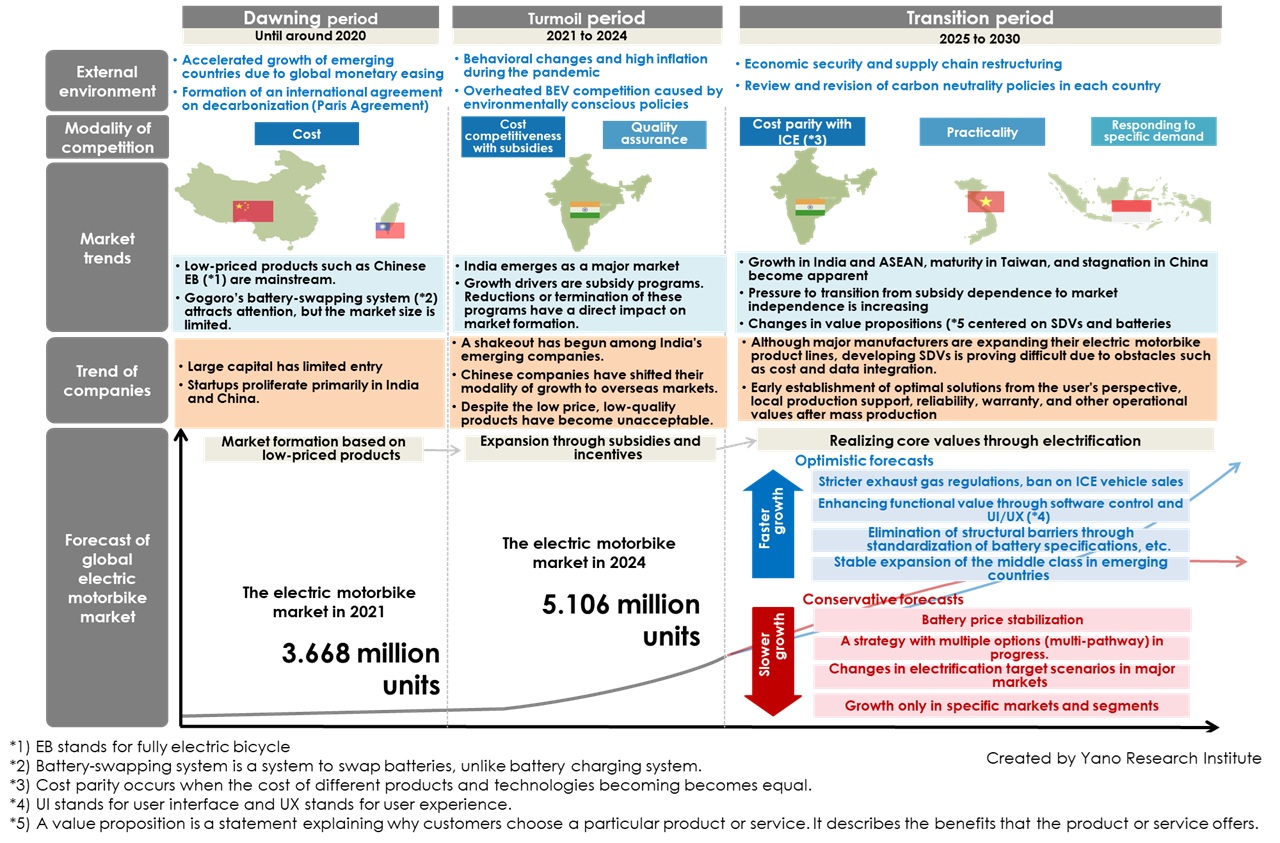
Keys to Spread Electric Motorbikes are SDVs and Separate Concepts between Vehicle and Battery
The business model of swappable batteries, which is based on the concept that separates vehicle and battery businesses, is key to the proliferation of electric motorbikes. Traditional battery swapping stations require enormous operating and maintenance costs, and these challenges have become apparent. Meanwhile, the growing commercial demand for electric motorbikes for delivery and sharing, which generate high utilization rates and profitability, indicates the need for a new business model for electric bikes that differs from those designed to satisfy large-scale individual needs.
Additionally, software-defined vehicles (SDVs) are a popular trend in four-wheelers and are expected to affect two-wheelers as well. However, the fully autonomous driving, which is the core value of SDVs, is difficult to achieve in two-wheelers due to limited space for embedding and cost. Some argue that SDVs cannot reap the benefits of electric motorbikes in terms of architecture (system composition and structure), such as a small number of electronic control units (ECUs) and a microcontroller-centered structure (a semiconductor chip that integrates a CPU, memory, and input/output features). Nevertheless, although advancements in electric motorbikes will be slower than those in four-wheelers, the potential of simpler hardware structures and lower costs are worth paying attention to for future developments.
Future Outlook
The global motorbike market is expected to grow steadily until 2030, primarily driven by India. In the long-term prospects until 2035, the South Asian markets centered on India are expected to mature, while new markets are likely to emerge in Africa and other regions, fueled by economic growth. Motorcycles are expected to play a key role in motorization in these countries.
Conversely, challenges have arisen regarding electric motorbikes. There have been reductions and discontinuations of subsidies in Europe and Taiwan, as well as rising safety concerns about battery fires in India. As the issue of resale prices for electric motorbikes has gained recognition in many countries including ASEAN nations, the momentum to unconditionally accept electric motorbikes has faded in price-sensitive Asian countries. These developments suggest an apparent difference from the “all-out electrification” trend of the early 2020s.
Another key factor in motorbike electrification is software-defined vehicles (SDVs). Although the SDV trend in the four-wheeler market has impacted on the two-wheeler market, various challenges remain in developing SDVs, such as how they will be used and the associated costs. There are also back-end challenges invisible to users. These challenges include IT and software development to support the underlying systems and services. Two-wheelers are expected to go through different electrification processes than four-wheelers.
Research Outline
2.Research Object: Motorbike manufacturers, suppliers, and related organizations
3.Research Methogology: Face-to-face interviews (including online interviews) by expert researchers, survey via telephone, and literature research
The Motorbike Market
A motorbike is defined as a two-wheeled vehicle that is usually powered by an internal combustion engine (ICE) or an electric motor.
This research discusses motorbikes with these types of engines and motors, excluding trikes (three-wheeled motorbikes) and two-wheeled motorbikes with sidecars. Though they are two-wheeled and motorized, pedal-assist electric bicycles, which use electric motors to assist pedaling power, and autonomous electric bicycles with a maximum speed of 25kph (16 mph) or less are excluded. E-scooters, which belong to the personal mobility category, are also excluded.
In this research, the optimistic forecast (expecting maximum growth) for the global electric motorbike penetration rate assumes that all issues that prevented the introduction of electric motorbikes, such as battery prices and charging infrastructure, will be resolved. It also assumes that mass production will price electric models competitively with existing motorbikes driven by ICEs. The conservative forecast (expecting minimum growth) assumes that no demand for electric motorbikes will be generated in markets where users tend to be price-sensitive, due to continuous high inflation rates and rising interest rates. This forecast also assumes the suspension of purchase incentives before the full launch of the electric motorbike market and changes in carbon neutrality scenarios that rely on methods other than electric vehicles (EVs), such as e-fuels (synthetic fuels produced from hydrogen and CO2) and biofuels produced by using plant-based ethanol as a raw material.
<Products and Services in the Market>
ICE-driven motorbikes and electric motorbikes
Published Report
Contact Us
The copyright and all other rights pertaining to this report belong to Yano Research Institute.
Please contact our PR team when quoting the report contents for the purpose other than media coverage.
Depending on the purpose of using our report, we may ask you to present your sentences for confirmation beforehand.