No.2008
Local Energy Management Business in Japan: Key Research Findings 2018
Local Energy Management Business in Japan: Key Research Findings 2018
Yano Research Institute (the President, Takashi Mizukoshi) has conducted a survey on the domestic local energy management business and has found out the current status and strategies at the enterprises in the business, and the transition of the market size for building the facilities and systems needed for local energy management.
Market Overview
While in normal circumstances those local energy management businesses optimally controls supply and demand of energy through CEMS (Community Energy Management System) aiming to save energy and reduce CO2 emissions, in emergency (i.e., at power failure) they contribute to the BCP (business continuity planning) at each local facility by supplying electricity independently using the cables that they operate. For local energy management business, enterprises are needed to build and introduce those facilities for generating renewable energy or for cogeneration, together with independently-managed electric cables, heat conduction pipes, CEMS, and etc. Therefore, the initial cost for the local energy management business is high. However, once started, the initial cost can be recovered by reducing energy costs through energy-saving operations, after which the economic effect continues.
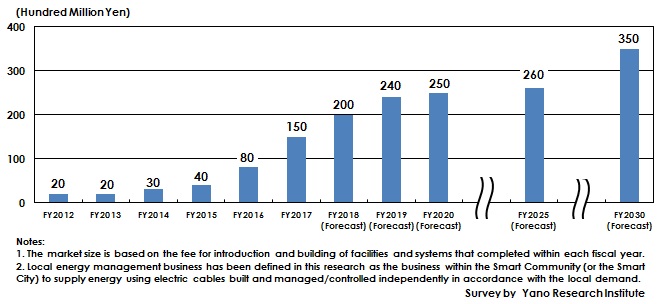
The market size for building the facilities and systems needed for local energy management (based on the cost of facilities and systems completed introducing or building within the concerned fiscal year) had been 2,000 million yen in FY2012 at the time when the domestic local energy management had launched, but was 15,000 million yen by FY2017 and is expected to attain 20,000 million yen by FY2018.
In order to establish the local energy management business, the demand for energy must be concentrated at that local areas, and it is needed to be able to supply and provide energy using low-cost systems. CEMS uses cloud technology so that it does not matter whether the facilities that accept energy are located at various places. However, diversely located facilities needing energy (electricity and heat) may require electric cables and heat conduction pipes to be constructed at larger distances and therefore may need larger costs, which may make the business economically difficult to sustain.
There are following three patterns for the energy demand to be concentrated:
1.At such a local government that supply electricity generated by locally-produced and consumed renewable energy to multiple public facilities built in adjacent to each other. (At local, suburban areas.)
2.At such a redevelopment project in the metropolitan area where electricity and heat are supplied through cogeneration systems and etc. to multiple high-rise buildings longitudinally located. (At urban development projects.)
3.In such an industrial area where electricity and heat are supplied through cogeneration systems and etc. to multiple factories located adjacent to each other with a great demand for energy. (At industrial areas where industrial parks and industrial complex exist.)
Noteworthy Topics
Specific power supply by means of independently operated cables has originally been existed in order to let industry parks and industrial complex to supply electricity that privately generated to other factories and affiliated companies. In the conventional specific power supply system, the suppliers needed to satisfy 100% of the demand from their power generation facilities and no backup power was available from electricity companies (general electricity utility). However, such restriction has been somewhat relieved in October 2012 to allow supplying of 50% or more of the demand. This has enabled non-utility power generation facilities to supply electricity to multiple buildings by adding transported backup power, which triggered the market of the local energy management business to be launched.
Research Outline
2.Research Object: Local energy management businesses, local governments, and consulting/engineering companies
3.Research Methogology: Face-to-face interviews by the expert researchers, survey via telephone/email, and literature search.
What is Local Energy Management Business?
Local energy management business has been defined in this research as the business within the Smart Community (or the Smart City) to supply energy using electric cables built and managed/controlled independently in accordance with the local demand.
Electric cables for sending and receiving electricity are built and managed by local energy management businesses. Such cables are able to supply electricity independently even at power failure.
Published Report
Contact Us
The copyright and all other rights pertaining to this report belong to Yano Research Institute.
Please contact our PR team when quoting the report contents for the purpose other than media coverage.
Depending on the purpose of using our report, we may ask you to present your sentences for confirmation beforehand.