No.3710
Energy Resource Aggregation Businesses (ERAB) Market in Japan: Key Research Findings 2025
ERAB Market Size Forecast to be 73.5 Billion Yen by FY2035
Yano Research Institute (the President, Takashi Mizukoshi) has surveyed the Energy Resource Aggregation Businesses (ERAB) market in Japan and has found out the markets of capacity/supply demand balancing/economic DR, trends of market players, and future outlook.
Market Overview
Energy Resource Aggregation Business (ERAB) is the business of aggregating energy resources (*1) from power generators and demand-side facilities for future use or to balance supply and demand when oversupply or shortage occurs. The intervention of energy resource aggregators results in the effective use of energy resources from demand side resources (DSR) or distributed energy resources (DSR) and enables various participants, including households, to engage in electricity transactions.
Electricity integrated by an aggregator is traded in the capacity market (the market for dispatchable power sources) for future use or as balancing power, or in the supply-demand balancing market as Replacement Reserve for FIT (RR-FIT). It is also used by electricity retailers for the economic DR (incentives) paid to contracted demanders who have cooperated in downward DR (*2) to prevent from imbalance between demand planning and actual demand or to avoid buying power from the wholesale market during the periods of supply shortage.
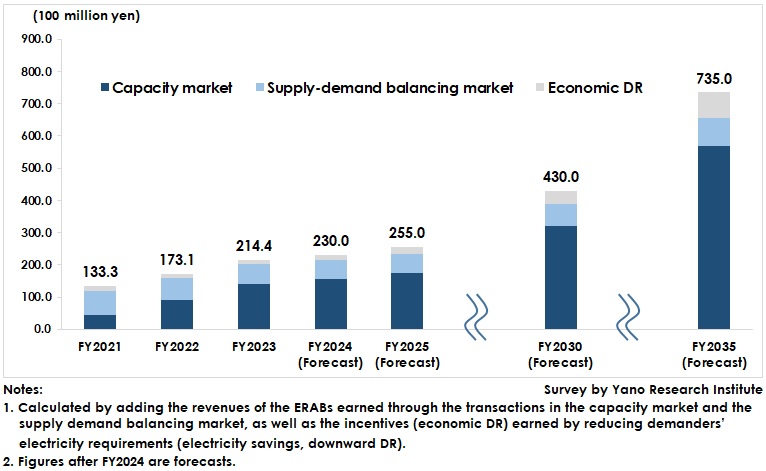
The ERAB market in this research is calculated by adding the revenues of the ERABs developing DR/VPP-related business earned through the transactions in the capacity market and the supply demand balancing market, as well as the incentives (economic DR) earned by reducing demanders’ electricity requirements (electricity savings, downward DR).
The size of the ERAB market in FY2022 has been estimated at 17.31 billion yen and has increased to 21.44 billion yen in FY2023, 123.9 % of the size in FY2022. The market is on an upward trend, with economic DR in the spotlight as a measure to promote decarbonization and counteract rising energy prices, mainly by high-voltage or special high-voltage demanders.
*1) Refers to power generation/storage/loading facilities such as solar PV, storage batteries, residential generators, manufacturing facilities, heat pump water heaters, electric vehicles, etc., connected at demanders’ receiving points.
*2) Refers to changing electricity demand patterns by controlling DSR. Downward DR means reducing electricity consumption (conservation) and upward DR means increasing electricity consumption.
Noteworthy Topics
Specification of “DReady System” Underway for Expanding Use of Low-Voltage Resources for DR
For further penetration of demand response (DR), the use of energy resources owned by low-voltage demanders, including general households, is expected to further increase.
However, the problem is that the DR potential per case is too low. In addition, DR based on behavioral incentives, such as asking demanders to conserve, tends to depend on changes in consumer behavior, which is a limitation to expanding DR.
Therefore, the role of an aggregator becomes more important, which is to remotely or automatically aggregate and control the power sources from multiple low-voltage demanders to use them as dispatchable power sources on demand or as RR-FIT in the capacity market. To achieve this, various resources used by low-voltage demanders need to be equipped with remote control capabilities as a standard. It is recommended as the “DRready system” in recent years.
As the direction of the DRready system, there is a plan to establish a mechanism to promote the installation of products that meet the requirements, referring to the Top Runner Programme, where the target energy consumption efficiency and the target fiscal year have been defined. The “DRready Study Meeting” initiated by the Agency for Natural Resources and Energy, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) will determine the target shipment ratio (the ratio of devices that meet the DRready requirements to the number of devices shipped) and the target fiscal year, based on the criteria of the DRready requirements set in the study meetings. Currently, the above discussion is underway for heat pump water heaters, with the target fiscal year likely to be FY2030, considering the early penetration and development cycle of the devices.
Future Outlook
In association with the revised Energy Rationalization Act that has been in effect since 2023, the reporting of the number of DR days implemented has been initiated by specific enterprises that consume 1,500 kiloliters or more of gasoline energy per year. In addition, DR participation is expected to expand among users of battery storage resources, as the volume of energy storage installations (for grid/stationary) is expected to increase.
Furthermore, the removal of barriers for low-voltage demander resources to enter the supply-demand balancing market and the implementation of the DRready system are planned in FY2026.
The ERAB market is forecast to reach 25.5 billion yen in FY2025, 43.0 billion yen in FY2030, and 73.5 billion yen in FY2035.
Research Outline
2.Research Object: Major utilities, new utilities, renewable energy generation/storage system engineering companies, energy management service providers
3.Research Methogology: Face-to-face interviews (including online) by expert researchers, and literature research
About Energy Resource Aggregation Businesses (ERAB)
In the electricity market in Japan, demand response (DR) initiatives using demand side resources (DSR) and the organization of virtual power plants (VPPs) consisting of distributed energy resources (DER) are in progress, due to the increasing penetration of photovoltaic power systems and other renewable energy sources, and the need for stable power supply even during the periods of soaring wholesale electricity prices or of supply shortages.
In the traditional method of reducing electricity demand by means of DR and VPPs, electricity retailers had to deal with it by contracting with large demanders to balance supply and demand. However, in the updated DR and VPPS, which are expected to expand, the intervention of ERAB operators aggregating many demanders will effectively utilize energy sources from DSR and DER, enabling diverse participants, including households, in electricity transactions.
Energy Resource Aggregation Businesses (ERAB) is the business of aggregating energy resources from power generators and demand-side facilities for future use or to balance supply and demand when oversupply or shortage occurs.
The Energy Resource Aggregation Businesses (ERAB) Market
The ERAB market in this research has been calculated by adding the revenues of the ERABs developing DR/VPP-related business earned through the transactions in the capacity market and the supply demand balancing market, as well as the incentives (economic DR) earned by reducing demanders’ electricity requirements (electricity savings, downward DR).
<Products and Services in the Market>
Energy Resource Aggregation Businesses (ERAB)
Published Report
Contact Us
The copyright and all other rights pertaining to this report belong to Yano Research Institute.
Please contact our PR team when quoting the report contents for the purpose other than media coverage.
Depending on the purpose of using our report, we may ask you to present your sentences for confirmation beforehand.