FX (Forex Margin Trading) Market: Key Research Findings 2010
Approaching to a turning point for newly defined FX trading
Research Outline
Yano Research Institute has conducted a study on the FX (Forex Margin Trading) market as described below.
1. Research period: June to July 2010
2. Research targets: Commodity futures dealers, dedicated FX trading companies, securities companies, Internet banking corporations, etc. in total of 96 enterprises
3. Research methodologies:
Face-to-face interviews with relevant personnel, supplemented by interviews via telephone and e-mail
< What is FX (Forex Margin Trading)? >
FX (Forex Margin Trading) in this research means the first financial product of foreign exchange trading in Japan for private investors that has emerged after the amendment of foreign exchange control law that went into effect in April 1998. The trading mechanism is that based on the margin deposit that works as collateral, much greater trade can be executed by means of leverage principle, and by settling the account for only the difference caused between the period of position opening and closing.
Summary of Research Findings
◆ Key Findings
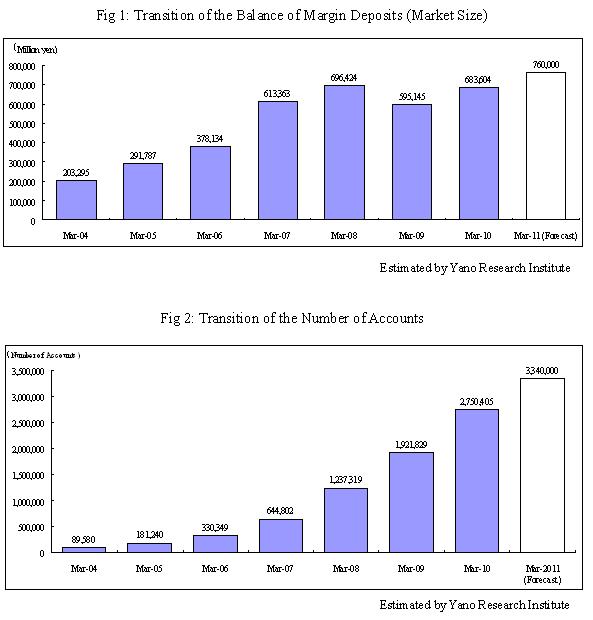
· FX market size (the balance of margin deposits) at the end of March 2010 was 683.6 billion yen, up 14.9 percent year-on-year
The balance of margin deposits has increased with majority of the enterprises due to their cultivation of new customers, although there are some who experienced negative growth. Especially, the growth of the Internet securities companies has been remarkable.
· The number of accounts at the end of March 2010 was 2.75 million, up 43.1 percent year-on-year
The demand of new investors has been stimulated by TV commercials and affiliate advertisements, lower spreads and enhancement of user-friendliness, which have led to the increase of user accounts.
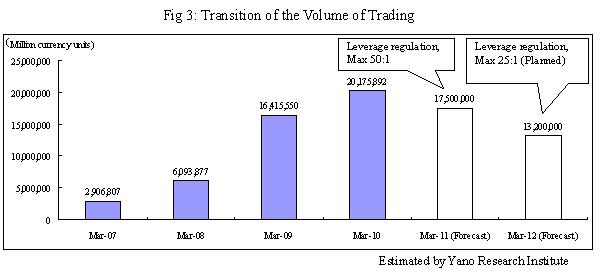
· The volume of trading in the year ended at the end of March 2010 was 2,017 trillion yen (1 million currency units are converted to 100 million yen), up 22.9 percent year-on-year
Due to the further evaluation of yen compared to the previous year, trading volume has decreased at quite a few enterprises. However, the enterprises with rapid increase of short-term trading due to their efforts on brand enhancement, higher leverage and lower spread offerings have contributed to increasing the total volume of trading in the industry.
· For the year ending at the end of March 2011, the market size (the balance of margin deposits) is expected to be 760 billion yen, with 3.34 million accounts and the trading volume of 1,750 trillion yen
The number of account openings is still increasing and the balance of margin deposits in an upward trend. However, due to the impacts of the leverage regulation introduced and enforced since August 2010, the volume of trading in the year ending at the end of March 2011 is expected to be 1,750 trillion yen (1 million currency units being converted to 100 million yen), and 1,320 trillion yen (ditto) in the year ending at the end of March 2012.
◆ Research Summary
1. History and background of the market
It has been more than 10 years since FX (foreign exchange margin trading) has become available as a financial product. Following the Revised Financial Futures Trading Act enforced in July 2005, the newly enacted Financial Instruments and Exchange Act has been enforced since September 2007. From August 2009, it has become mandatory to keep the customers’ margin deposits in trust and to implement “loss-cut” system. Further, the phased implementation of leverage lowering regulation enforced in August 2010 has forced those enterprises who can not cope with the reinforced regulations to withdraw from the market.
At the same time, the competition on lowering the spreads has become intensive in view of improving their product competitiveness. And the competition on attracting new customer groups has become severe as increasing number of enterprises enter into the exchange trading in addition to the existing OTC trading operations.
During these 2-3 years under the market with a trend of higher yen, the investors’ style of investment has been changing from mid-to-long term investments to short-term and ultra-short-term investments, while being buffeted continuously, by the prime loan issues, Lehman Shocks, Dubai Shocks, and the financial shock of Greek in May 2010.
Among the 96 financial product trading firms that offer FX trading service at the end of July 2010 identified as the result of this research, the securities companies have out-numbered the dedicated FX traders for the first time in the FX industry. (Total 96 firms consisting of 43 dedicated FX traders, 44 securities companies, 5 futures companies and 4 banks)
2. Market overview
The balance of margin deposits had decreased in the year ended at the end of March 2009 for the first time, due to the rapid and steep escalation of yen caused by the Lehman Shocks in the autumn of 2008, which, however, has recovered quickly in the year ended at the end of March 2010, to 683.64 billion yen, up 14.9 percent compared to the previous year, owing to the progress of new customer attractions implemented and achieved by the enterprises in the market. The balance of margin deposits has increased with majority of the enterprises, although there are some who experienced negative growth. Especially, the growth of the Internet-based securities companies has been remarkable.
The number of accounts has been steadily increasing, in spite of the various social factors mentioned above, and reached to 2,750,405 accounts at the end of March 2010, up 43.1 percent from the previous year. The number of account increase has been supported, in addition to the implementation of seminars for investors and campaigns such as cash-backs, by the improvement of user-friendliness such as the introduction of high-specs products with narrower spreads and user-friendly trading systems.
The volume of OTC trading in the year ended at the end of March 2010 was estimated to be 2,017 trillion 589.2 billion yen (1 million currency units being converted to 100 million yen), up 22.9 percent from the previous year. Although quite a few enterprises have experienced the decrease in the volume of trading, those who have been working on the improvement of their brand, and competitiveness with higher leverage and lower spreads, have achieved the increase in the volume of trading, and contributed to increasing the total volume of trading in the industry.
3. Market forecast
As the balance of margin deposits and the number of accounts will continue to increase, the market size (the balance of margin deposits) in the year ending at the end of March 2011 is estimated to be 760 billion yen, and the number of accounts 3.34 million.
The volume of trading in the year ending at the end of March 2011, in the meantime, is expected to be 1,750 trillion yen (1 million currency units being converted to 100 million yen), decrease by 13.3 percent compared to the previous year, with the consideration of the impacts of leverage regulations introduced, as well as the expected increase of trading due to the high yen caused by the “Greek Shock” occurred in May 2010. The volume of trading in the year ending at the end of March 2012 with full-fledge implementation of the leverage regulations is expected to further decrease to 1,320 trillion yen (ditto), decrease by 24.6 percent from the preceding year, which is the decrease by 34.6 percent compared to the year ended at the end of March 2010.
Published Report
Report Title: Foreign Exchange Margin Trading Market 2010
*The information provided in the "Research Summary" is what is as of the date of announcement and could be altered or renewed without any prior notice.